Deploying an n8n AI Chatbot Agent on AWS ECS with Amazon Bedrock
Deploying an n8n AI Chatbot Agent on AWS ECS with Amazon Bedrock

Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. System Architecture
- 3. Load Balancer Creation
- 4. ECS Cluster and Service
- 5. Bedrock and IAM User
- 6. n8n Agent Setup
- 7. Conclusion
1. Introduction
N8n is a popular workflow automation tool renowned for its robust integration capabilities and built-in AI features. This article provides step-by-step guidance on constructing a self-hosted AI chatbot agent by leveraging n8n in conjunction with Amazon Bedrock's AI models. We will containerize the application using AWS Elastic Container Service (ECS), ensuring scalability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
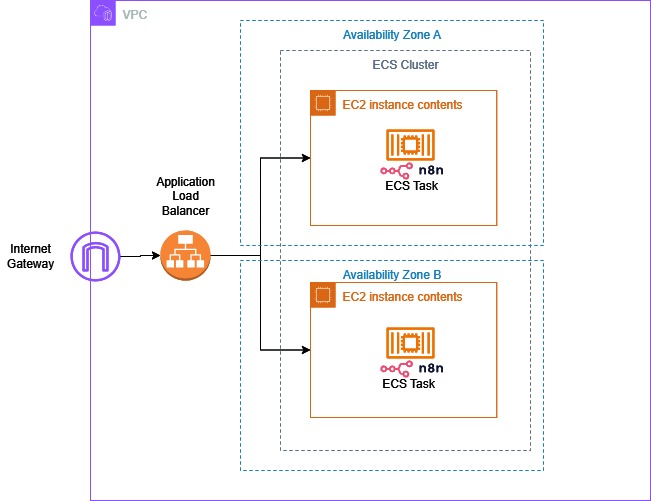
2. System Architecture
The system is designed to ensure high availability, efficient traffic management, and seamless integration of AI-driven workflows. Below are the key components and their roles in the architecture:
- Application Load Balancer (ALB): Routes traffic to ECS tasks.
- ECS Cluster: Manages container orchestration (using EC2 instances in this guide).
- ECS Task Definitions: Configures the n8n container.
- ECS Service: Runs and scales tasks.
- n8n: Core workflow automation platform for the AI chatbot.
- Amazon Bedrock: Provides foundation models (e.g., Anthropic Claude, Amazon Nova Pro).
3. Load Balancer Creation
- Navigate to EC2 > Load Balancers > Create Load Balancer.
- Select Application Load Balancer.
- Configure as Internet-facing with IPv4.
- Select the appropriate VPC and at least two subnets (across Availability Zones).
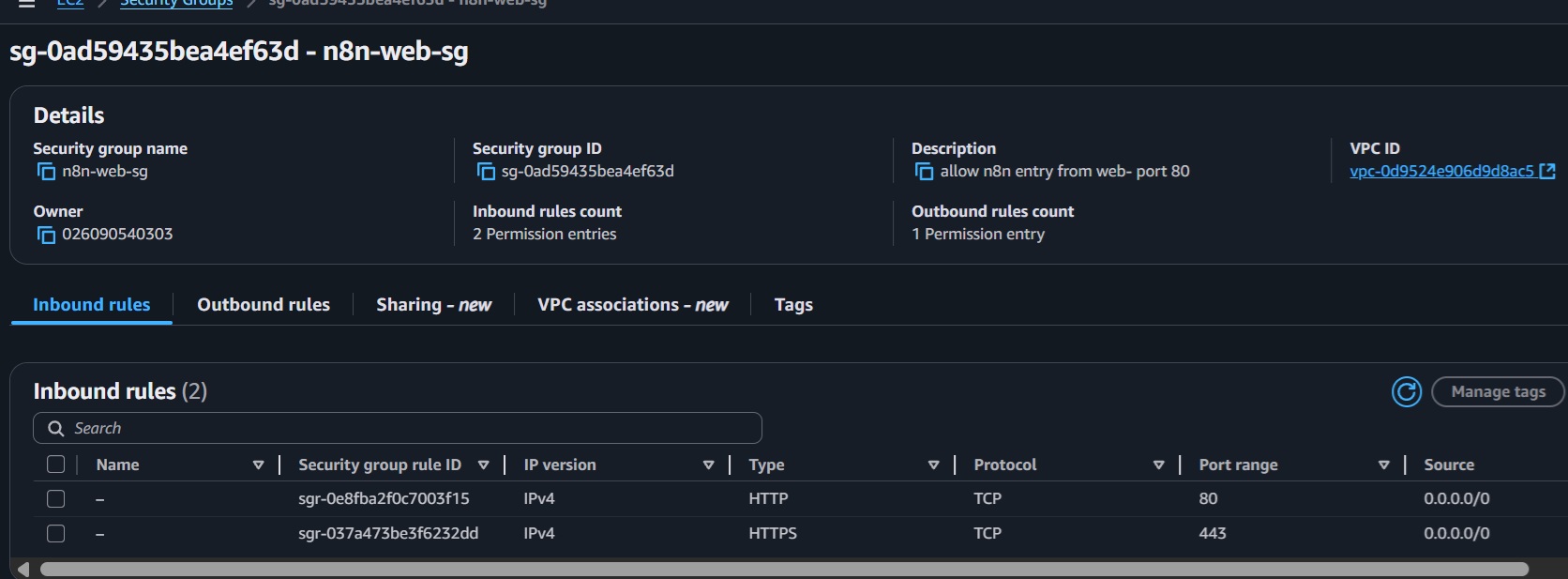
- Create a new security group (
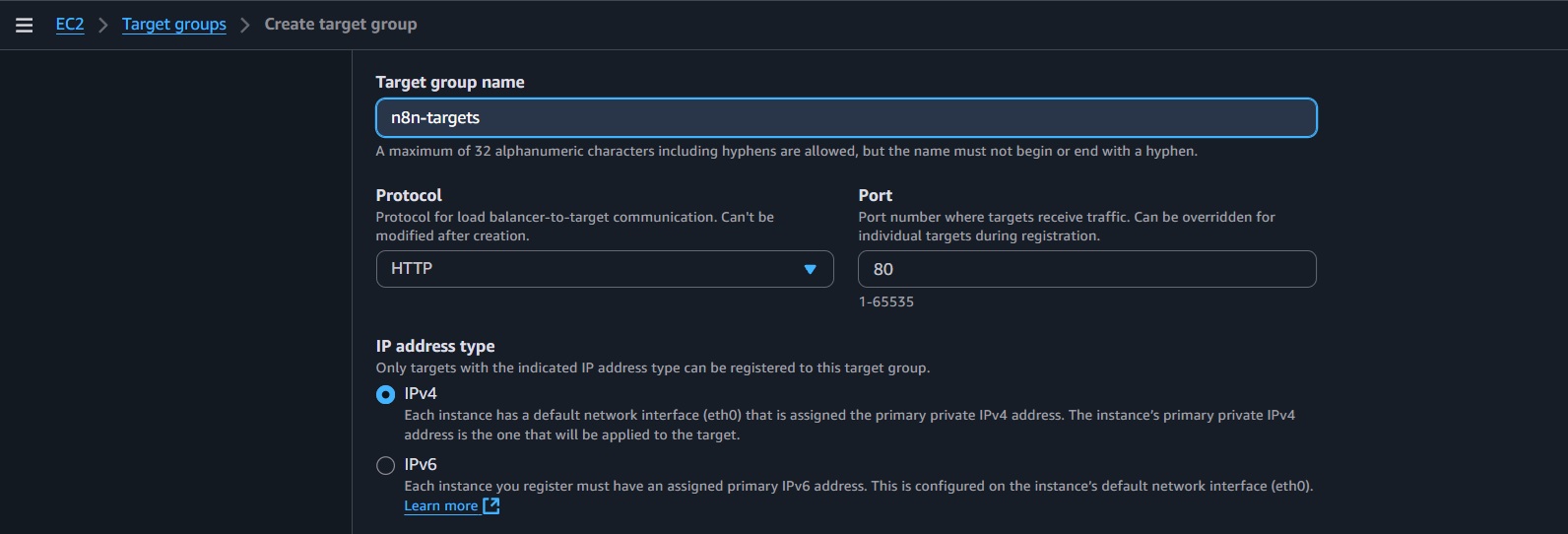
n8n-web-sg) with inbound rules for HTTP (80) and HTTPS (443) from0.0.0.0/0. - Add listeners for HTTP:80 and HTTPS:443; create a target group (
n8n-targets). - Set target type to INSTANCE while skipping the register targets details.
- Configure health check path:
/healthz. - Click Create to create the ALB.
Note: For HTTPS, configure an SSL certificate via AWS Certificate Manager (not covered here).
4. ECS Cluster and Service
This section guides you through creating an ECS cluster and service. These components manage the containerized n8n application for scalability and reliability.
Create ECS Cluster
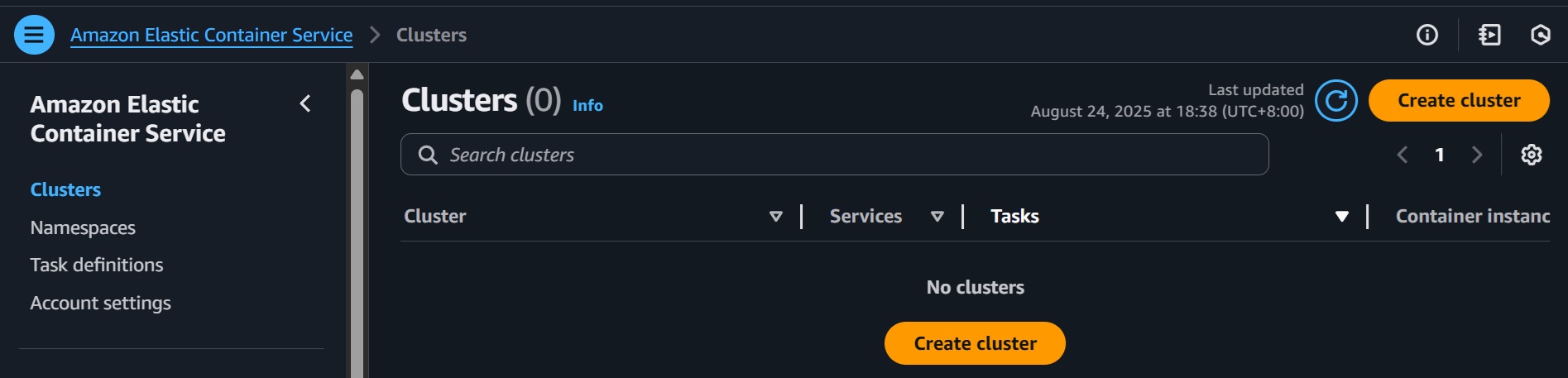
- Go to ECS Console > Clusters > Create Cluster.
- Name:
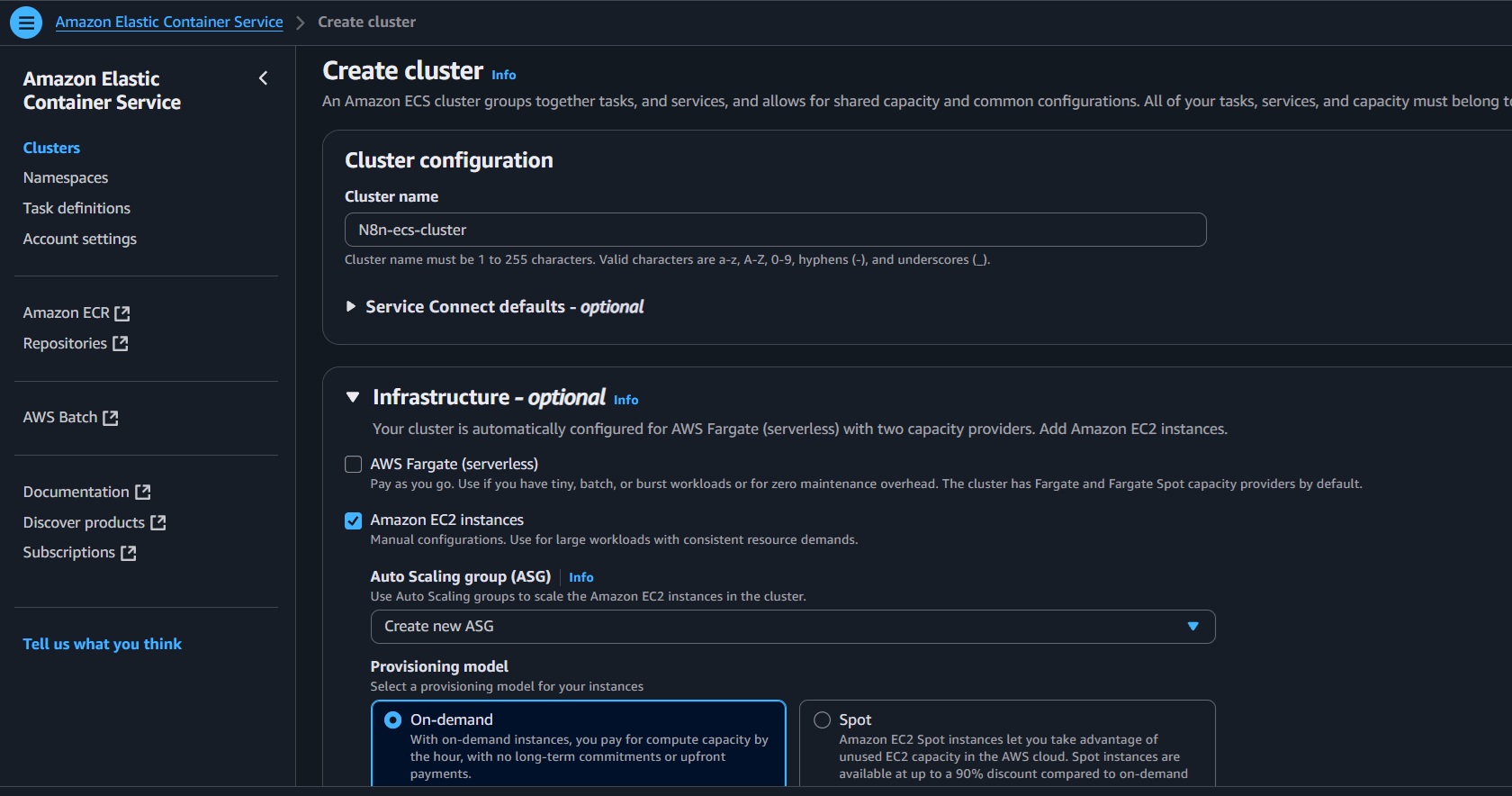
n8n-ecs-cluster. - Select EC2 (not Fargate).
- Choose create a new Auto Scaling Group (ASG).
- Choose Amazon Linux 2023 and an instance type (e.g.,
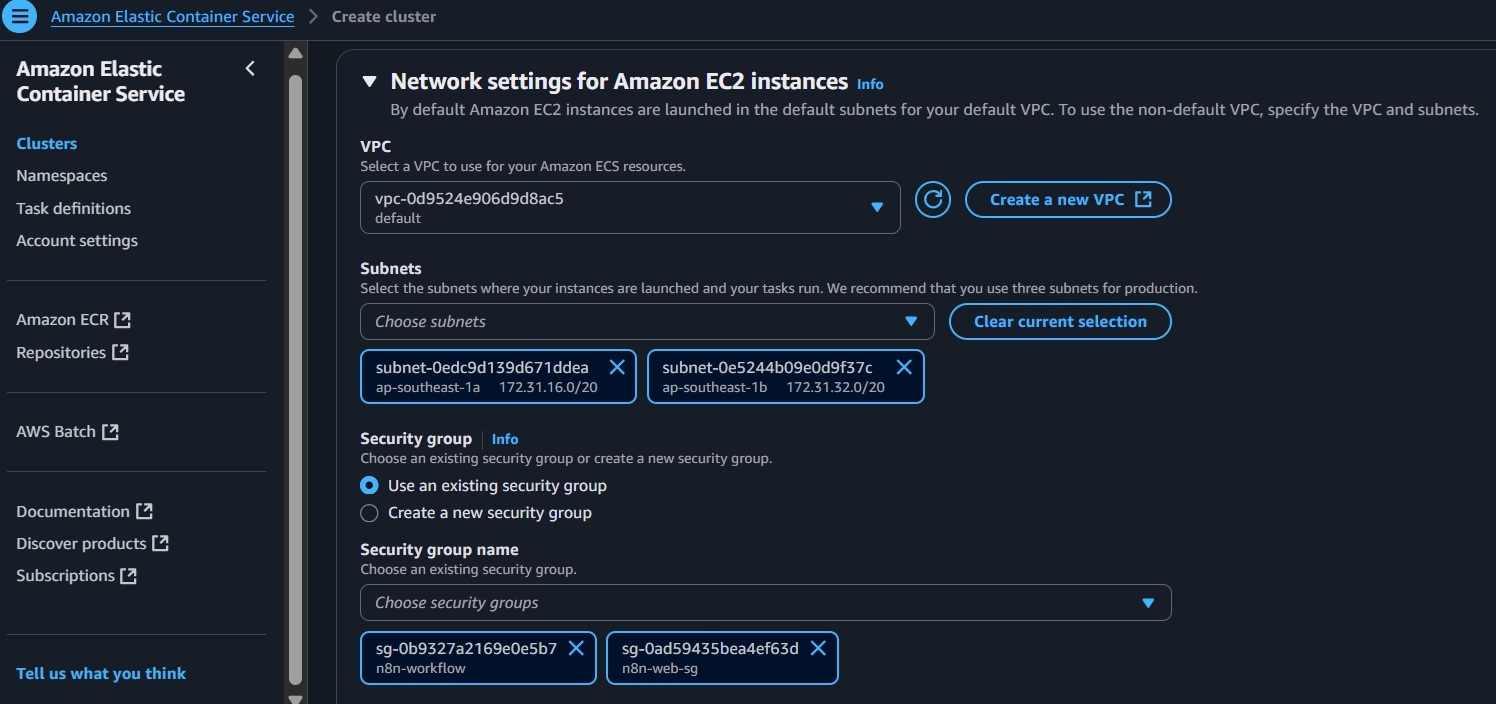
t3.micro). - Select the same VPC and subnets as the ALB.
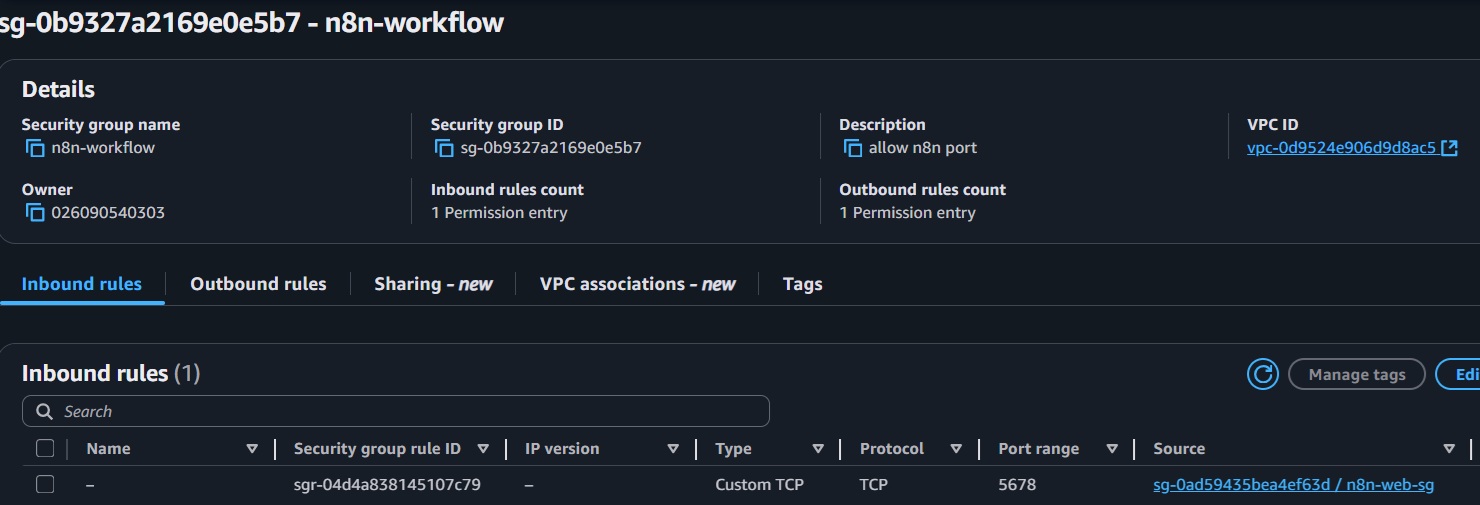
- Create a new security group (
n8n-workflow) with an inbound rule for port 5678 from the ALB security group. - Click Create to create the ECS Cluster
Create Task Definition
- Go to ECS Console > Task Definitions > Create new Task Definition.
- Use JSON to define the task:
{
"family": "n8n-task",
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"cpu": 0,
"environment": [
{
"name": "GENERIC_TIMEZONE",
"value": "UTC"
},
{
"name": "N8N_HOST",
"value": "0.0.0.0"
},
{
"name": "N8N_SECURE_COOKIE",
"value": "false"
},
{
"name": "N8N_PORT",
"value": "5678"
},
{
"name": "N8N_PROTOCOL",
"value": "http"
}
],
"essential": true,
"image": "n8nio/n8n:latest",
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awslogs",
"options": {
"awslogs-group": "/ecs/n8n",
"awslogs-create-group": "true",
"awslogs-region": "your-region",
"awslogs-stream-prefix": "ecs"
}
},
"mountPoints": [],
"name": "n8n",
"portMappings": [
{
"containerPort": 5678,
"hostPort": 5678,
"protocol": "tcp"
}
],
"systemControls": [],
"volumesFrom": []
}
],
"taskRoleArn": "arn:aws:iam::account-id:role/ecsTaskRole",
"executionRoleArn": "arn:aws:iam::account-id:role/ecsTaskExecutionRole",
"networkMode": "bridge",
"volumes": [],
"placementConstraints": [],
"requiresCompatibilities": [
"EC2"
],
"cpu": "512",
"memory": "756"
}
- Replace
<your-region>with your AWS region (e.g.,us-east-1) and<account-id>with your AWS account ID. - Ensure
ecsTaskExecutionRoleandecsTaskRolehave permissions for CloudWatch Logs for troubleshooting. - Click Create.
Create ECS Service
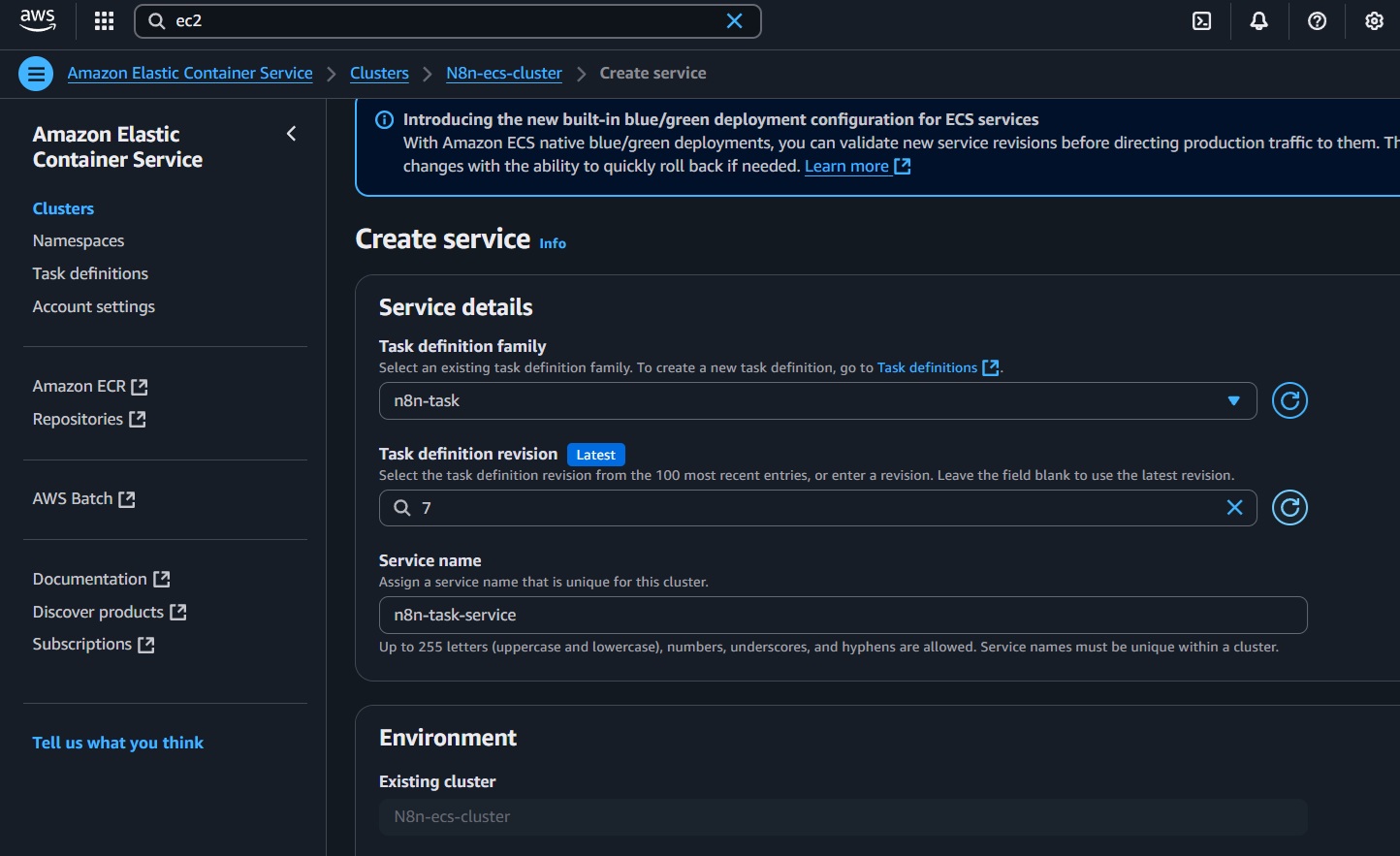
- Go to ECS Console > Clusters > n8n-ecs-cluster > Services > Create.
- Select task definition:
n8n-task(latest revision). - Service name:
n8n-task-service. - Set desired tasks (e.g., 1).
- Use default capacity provider strategy.
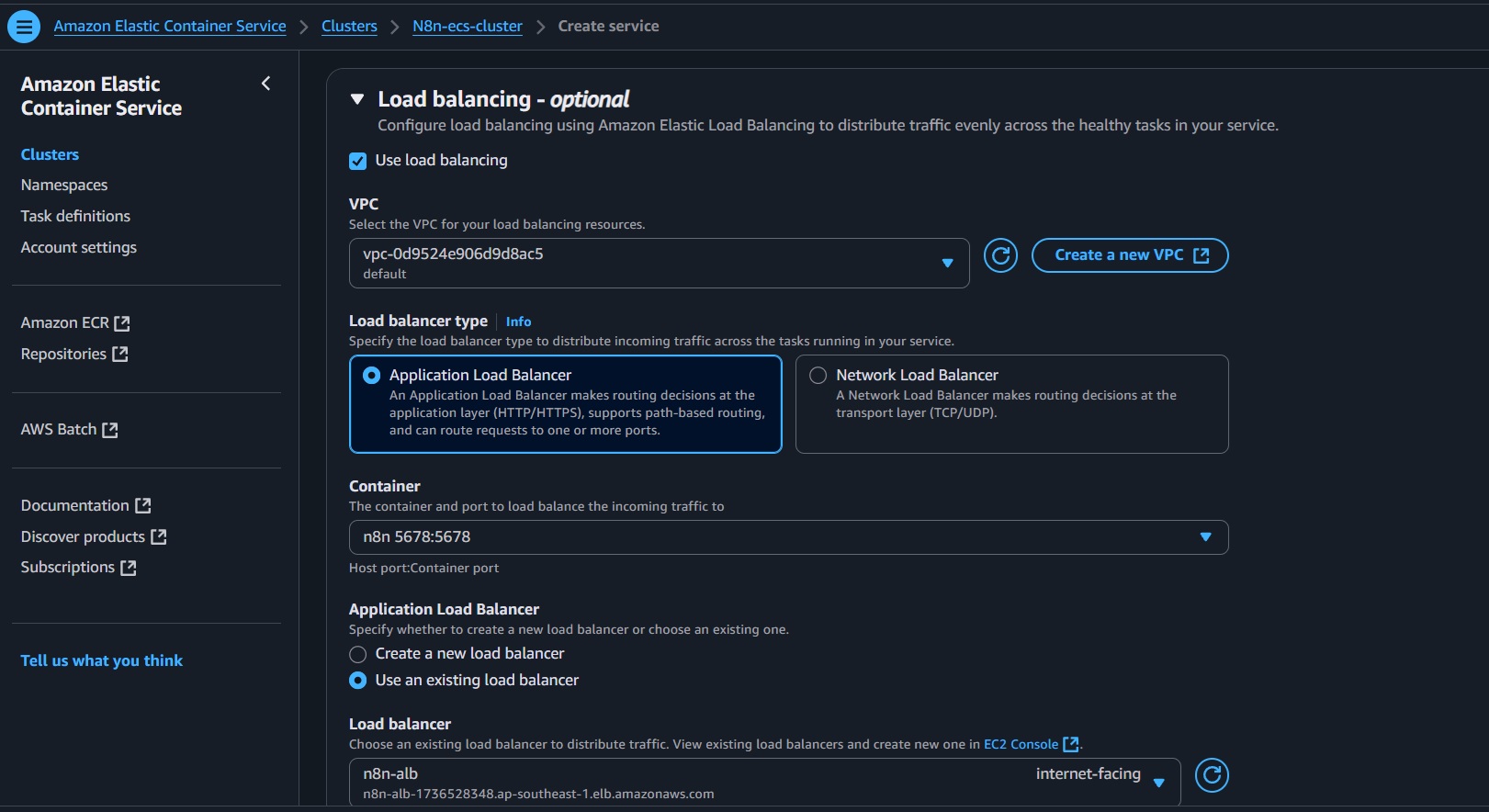
- Enable load balancing; select the existing ALB and target group (
n8n-targets). - Select to use the existing listeners (e.g. HTTP/80).
- Click Create.
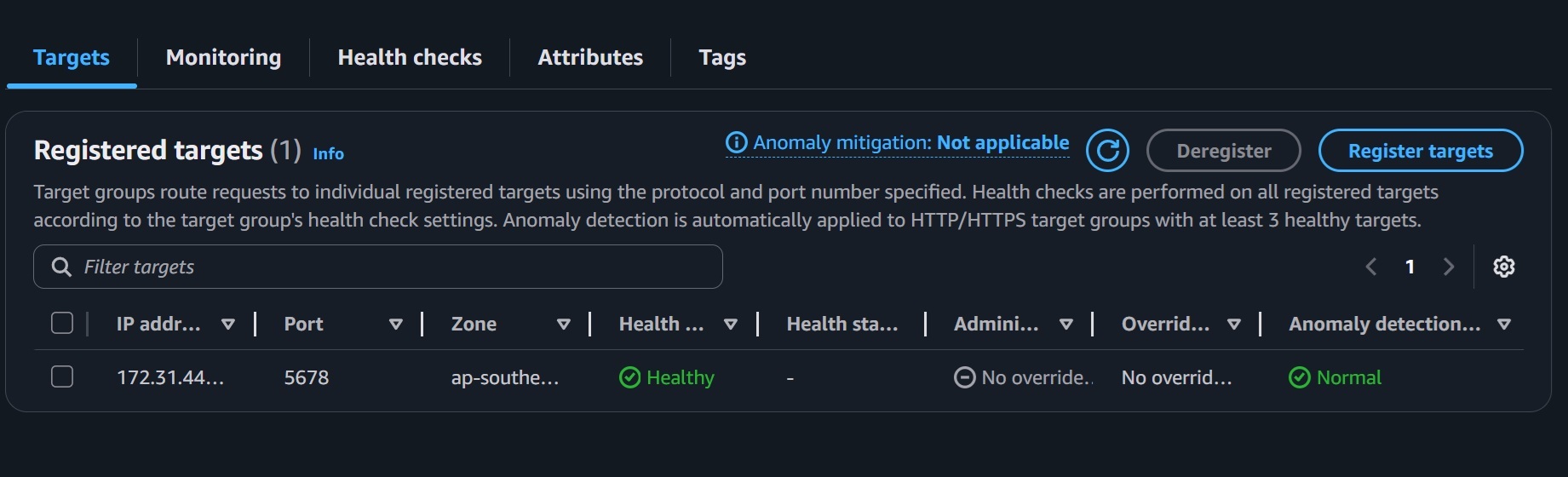
- Verify the task is running and the ALB target group shows Healthy status for the task's IP.
5. Bedrock and IAM User
This section covers setting up an IAM user for Amazon Bedrock. It ensures secure access to Bedrock’s AI models for the n8n chatbot.
Create IAM User
- Go to IAM Console > Users > Create User.
- Name:
bedrock-user. - Select Programmatic access.
- Skip adding to groups or attaching policies.
- Click Create User.
Create Access Key
- Open
bedrock-userdetails. - Go to Security credentials > Create access key.
- Select Application running outside AWS.
- Click Create and save the Access Key ID and Secret Access Key (download CSV).
Create Inline Policy for Bedrock
- In
bedrock-userdetails, go to Permissions > Add permissions > Create inline policy. - Use JSON editor and input:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"bedrock:InvokeModel",
"bedrock:InvokeModelWithResponseStream",
"bedrock:ListFoundationModels",
"bedrock:GetFoundationModel"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
- Name policy:
BedrockDeveloperPolicy. - Click Create policy.
6. n8n Agent Setup
This section details the configuration of the n8n application. It includes setting up the account and creating an AI chatbot workflow.
- Access n8n via the ALB DNS name (e.g.,
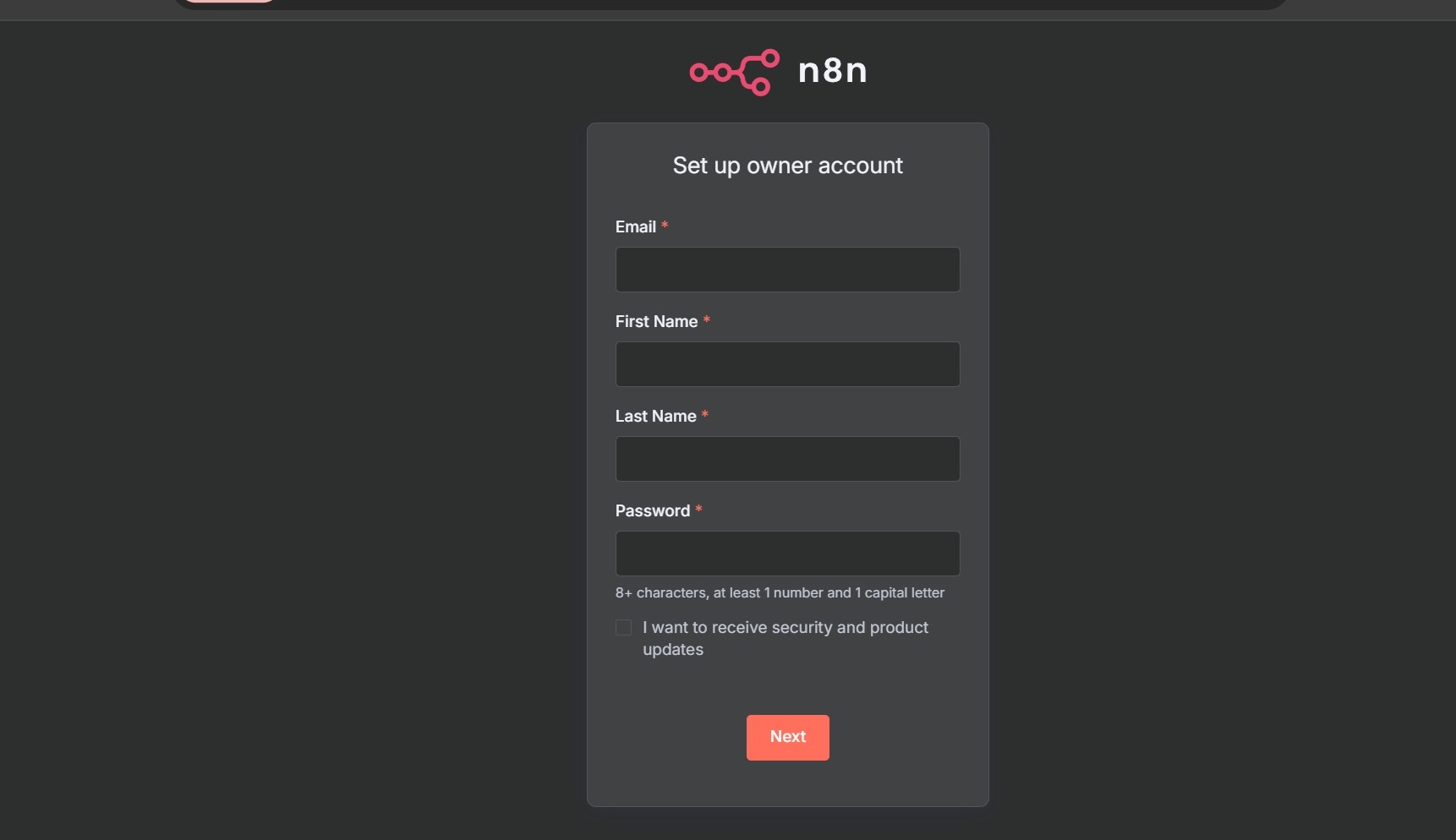
http://<alb-dns-name>). - Set up n8n account: Enter email, first name, last name, and password.
- Click Get started.
- Request a trial key from n8n (sent via email).
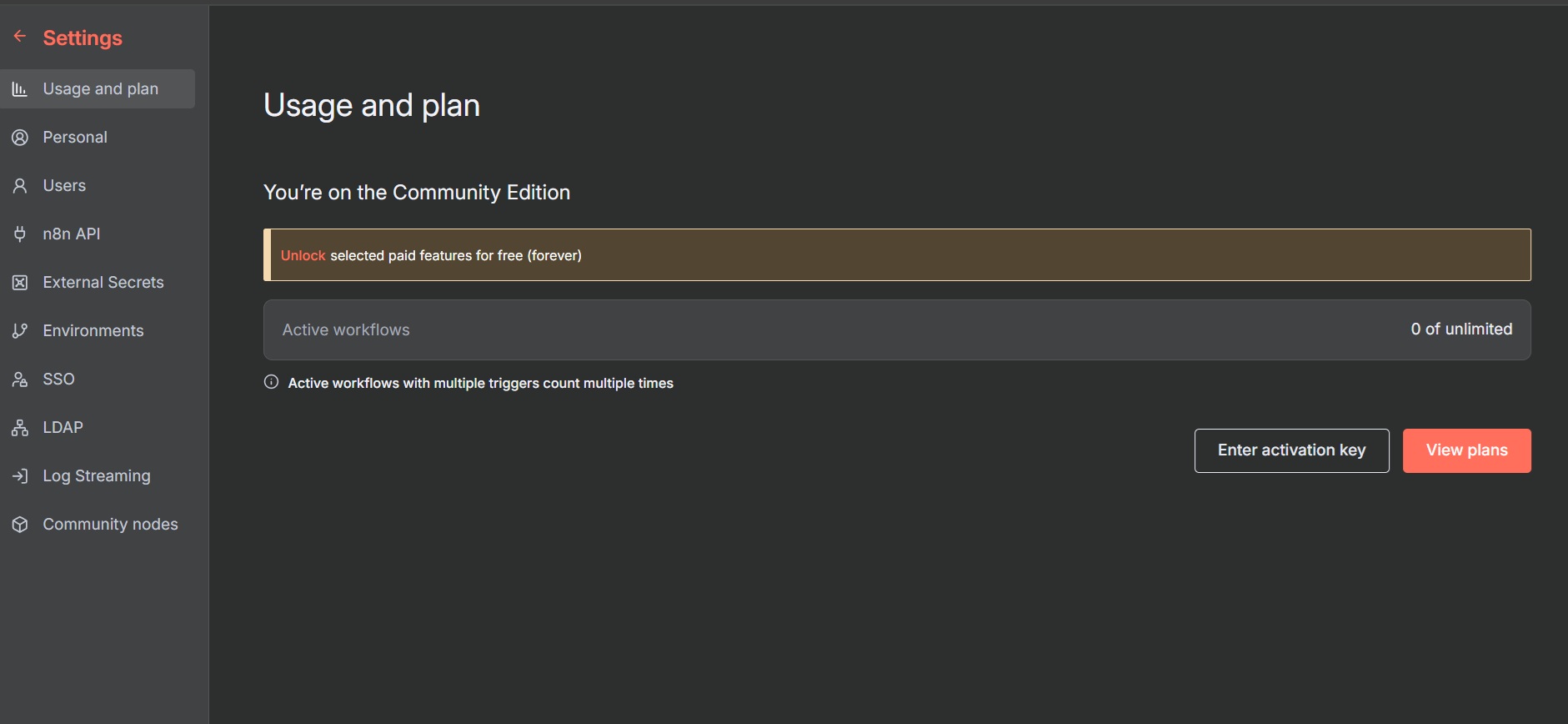
- Go to Settings > Usage and Plan > Enter activation key to activate the license.
Create Workflow
- On the n8n homepage, click Create Workflow.
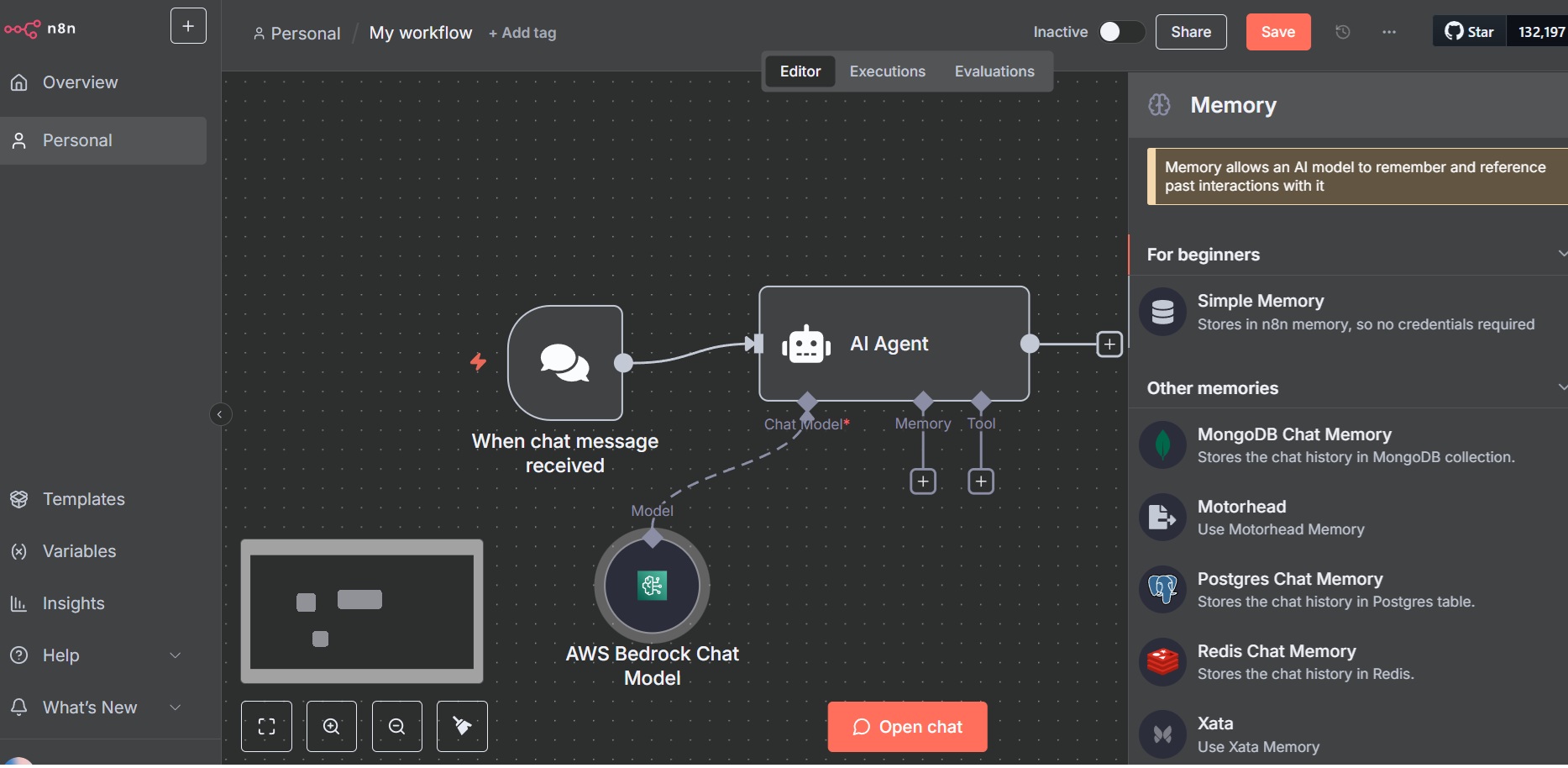
- Click Add first step and select AI Agent.
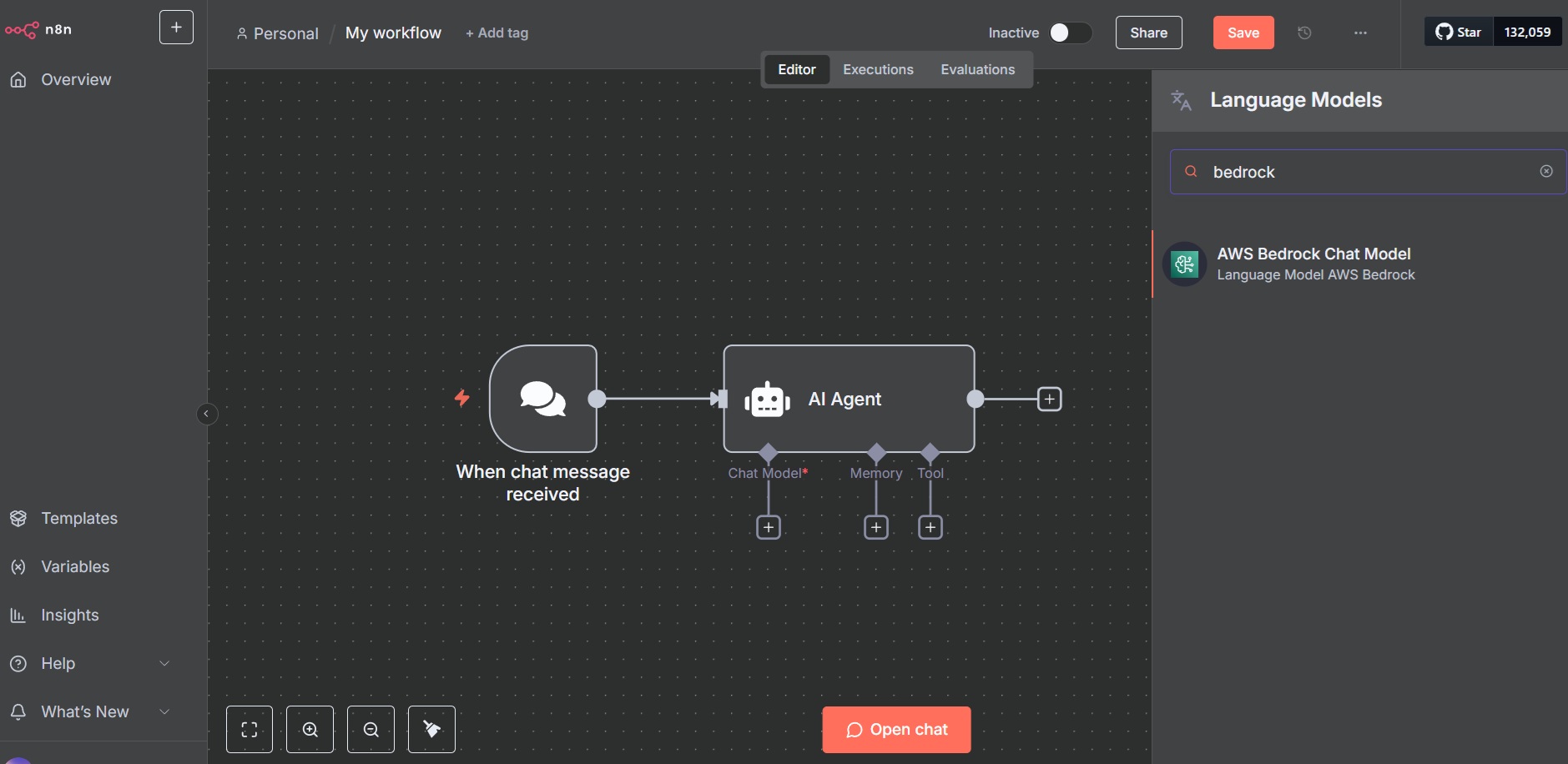
- In Chat model, select AWS Bedrock Chat Model.
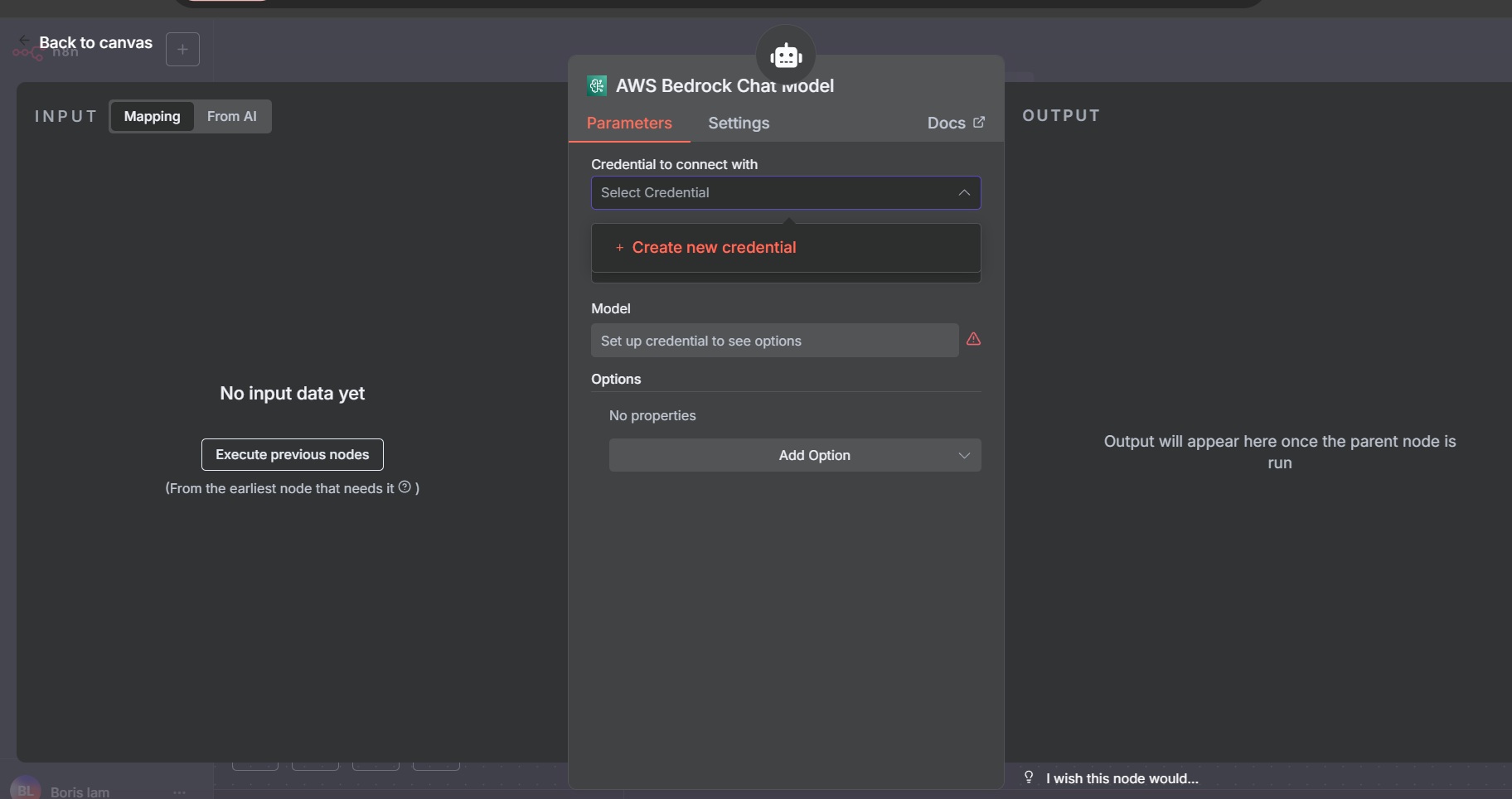
- Click Create new credential and input the Access Key ID and Secret Access Key.
- Select desired Bedrock model (e.g., Anthropic Claude).
- In the AI Agent, configure Memory and select Simple Memory.
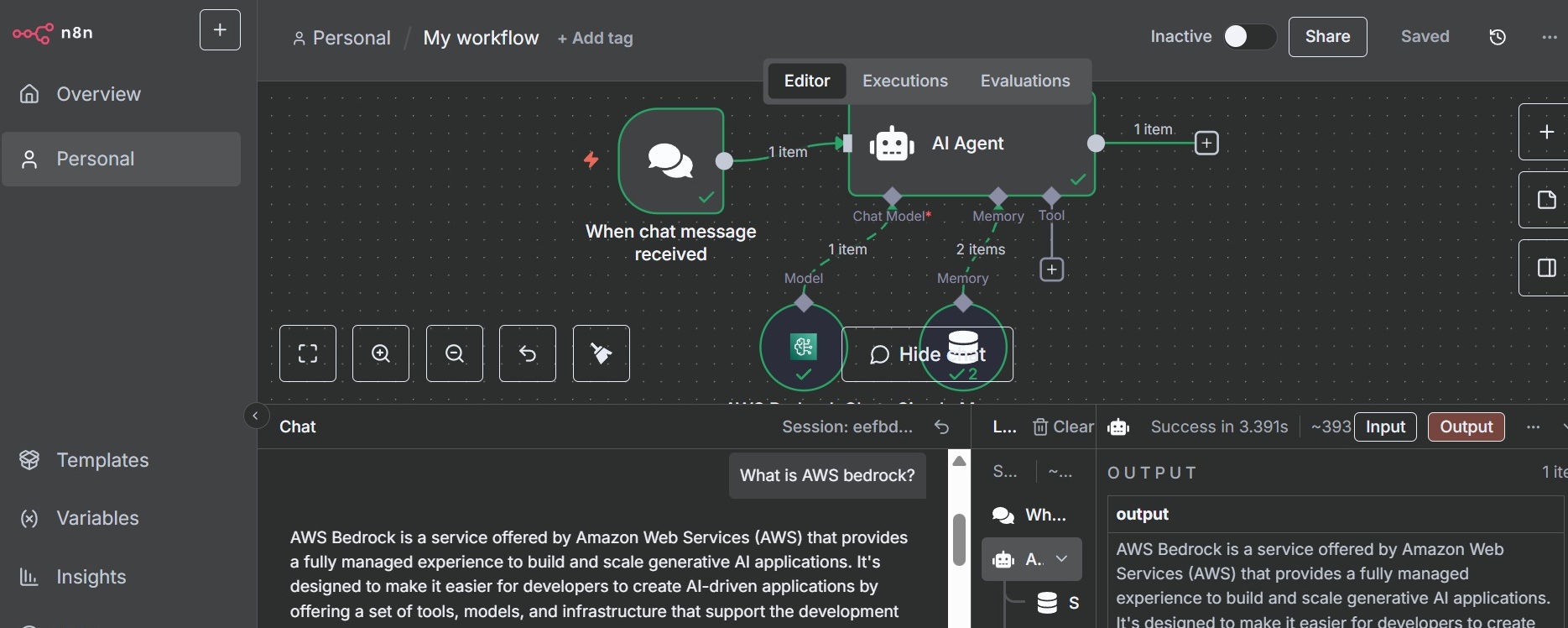
- Click Open Chat to test the chatbot. Now you can interact with the AI chatbot agent.
7. Conclusion
You have successfully built and deployed an AI chatbot agent using n8n on AWS ECS, integrated with Amazon Bedrock for advanced AI capabilities. n8n’s flexibility enables enhancements like email integration or a vector database for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). The agent can also be exposed as an API via webhooks.
It’s important to note that, in the current setup, workflow data is stored locally within the container’s filesystem. As a result, any data may be lost if the ECS task or cluster restarts. To ensure data persistence and production readiness, we recommend using Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) for durable storage of n8n workflows and configurations.
In the next article, we will explore integrating n8n with EFS and Amazon Aurora to create a RAG-enabled chatbot. Stay tuned!
